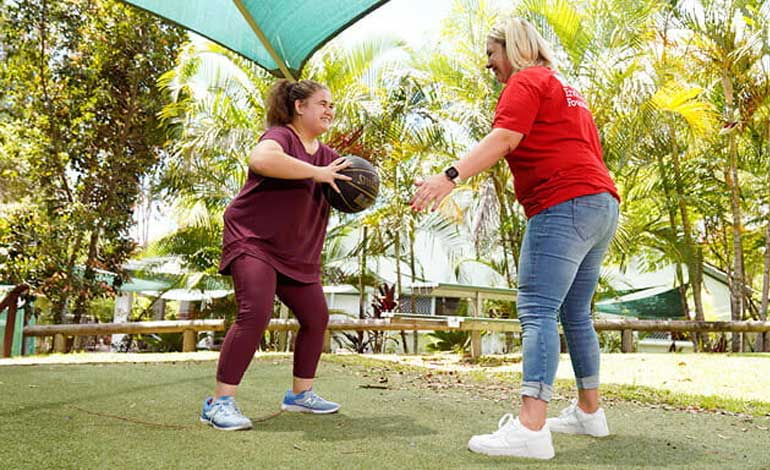
A Simple Guide to Developing Life Skills for People with Disabilities
Helping a person with a disability develop life skills is essential for fostering independence and enhancing their quality of life. Life skills enable individuals to perform daily tasks, engage with their community, and live more self-sufficiently. While everyone’s abilities and needs are different, there are simple and effective methods that can support the development of these important skills.
This blog provides practical and straightforward ways to help people with disabilities build essential life skills through structured approaches, hands-on activities, and positive reinforcement.
- Break Tasks into Simple Steps
Many life skills, such as cooking, cleaning, or personal hygiene, can seem overwhelming when viewed as a whole. Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps is a simple and effective way to make the learning process easier.
Here’s how to break down tasks:
- Identify the task: Start with a specific skill, such as brushing teeth, making a sandwich, or using public transport.
- List the steps: Write down or verbally explain the steps required to complete the task. For example, for brushing teeth, the steps might include picking up the toothbrush, applying toothpaste, brushing, rinsing, and cleaning up.
- Demonstrate and practice: Show the individual how to complete each step, and then have them practice with guidance. Repeat the steps as needed until they feel confident performing the task independently.
By focusing on one step at a time, the person can build confidence and gradually develop the ability to complete the full task on their own.
- Use Visual Supports and Checklists
Visual aids, such as pictures, charts, or written instructions, can help individuals with disabilities better understand and remember the steps involved in daily activities. These tools can provide clear guidance and serve as a helpful reference when learning new skills.
Here are ways to use visual supports:
- Create picture schedules: For individuals who benefit from visual learning, create a daily routine chart using pictures or symbols. For example, a morning routine chart might include images for brushing teeth, getting dressed, and eating breakfast.
- Checklists: For more complex tasks, use written or picture-based checklists. This allows the person to follow a sequence of steps and check off each step as they go along, making the process more structured and achievable.
- Label objects: Label household items such as drawers, containers, or cleaning supplies with pictures or words, so the person knows where things belong and can find what they need easily.
Visual supports are especially helpful for individuals who process information better through images or those who may need reminders for multi-step tasks.
- Practice Through Real-Life Scenarios
The best way to learn life skills is by practicing them in real-life situations. By creating opportunities to apply new skills in everyday settings, individuals can gain confidence and become more comfortable with their abilities.
Here’s how to incorporate real-life practice:
- Cooking meals together: Involve the person in simple meal preparation tasks, such as measuring ingredients, stirring, or setting the table. Start with easy-to-follow recipes and gradually increase the complexity as their skills improve.
- Shopping trips: Take the individual to the grocery store and involve them in selecting items, managing a budget, or paying at the checkout. This helps develop both practical and social skills.
- Personal care routines: Encourage the individual to take part in personal care tasks such as brushing their hair, putting on clothes, or showering. Provide guidance as needed but allow them to perform tasks independently when possible.
Real-life practice not only reinforces learning but also helps the individual feel more confident and capable in handling day-to-day activities.
- Encourage Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
Developing life skills isn’t just about learning specific tasks; it’s also about fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities. Encouraging a person with a disability to make choices and solve problems helps them build independence and take ownership of their decisions.
Here’s how to support problem-solving:
- Offer choices: Present two or three options when it comes to daily activities. For example, ask if they would prefer to wear a blue shirt or a red shirt, or if they’d like toast or cereal for breakfast. Offering choices helps the person practice decision-making in a low-pressure environment.
- Ask guiding questions: When faced with a problem, ask questions that encourage the individual to think through the solution. For example, if they forget where an item belongs, ask, “Where do we usually keep the spoons?” instead of immediately providing the answer.
- Celebrate success: Acknowledge their efforts and successes, even if the outcome isn’t perfect. Positive reinforcement builds confidence and encourages further problem-solving.
Fostering decision-making and problem-solving skills empowers individuals to take more control over their lives and improves their ability to handle new or unexpected situations.
- Build Social and Communication Skills
Social interactions and communication are important aspects of daily living. Teaching individuals with disabilities how to effectively communicate their needs, interact with others, and navigate social situations is essential for their personal growth and community participation.
Here’s how to develop social and communication skills:
- Role-playing scenarios: Practice common social situations, such as greeting someone, asking for help, or ordering at a café, through role-playing. This allows the individual to rehearse conversations and build confidence.
- Encourage communication: Whether the person communicates verbally, through sign language, or by using communication aids, encourage them to express their needs and preferences. Give them opportunities to ask for assistance or make choices throughout the day.
- Join group activities: Encourage participation in group activities, such as community classes, sports, or social events. Engaging in group settings helps individuals practice communication, cooperation, and social etiquette.
By developing social skills, individuals can engage more comfortably in their communities and build meaningful relationships with others.
- Create a Structured and Supportive Environment
Creating a structured and supportive environment is key to helping individuals with disabilities thrive in their learning. Consistent routines and clear expectations provide a sense of security, making it easier to learn and retain new skills.
Here’s how to create structure:
- Establish routines: Set up consistent daily routines for activities such as meals, personal care, and bedtime. Routine helps individuals feel more secure and understand what is expected of them each day.
- Provide a calm environment: Minimize distractions and create a calm, organized space for learning and practicing life skills. This helps individuals focus on the task at hand.
- Be patient and supportive: Learning new skills takes time, and progress may be slow at first. Offer encouragement, celebrate small victories, and provide support without taking over the task completely.
A supportive environment fosters learning and growth, giving the individual the confidence they need to develop and maintain life skills.
- Use Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a powerful tool for motivating individuals to learn and practice life skills. By recognizing and rewarding progress, you can encourage continued effort and build a positive association with the learning process.
Here are simple ways to use positive reinforcement:
- Offer praise: Verbal praise such as “Great job!” or “You did it!” can boost the individual’s confidence and reinforce their progress.
- Use rewards: Small rewards, such as a favorite snack or activity, can motivate individuals to keep practicing a skill. For example, if they successfully complete a task like tidying up, offer a reward as positive reinforcement.
- Celebrate milestones: When the person masters a new skill, celebrate the achievement with them. This recognition helps them feel proud of their accomplishments and motivates further learning.
Positive reinforcement helps build self-esteem and encourages the continued development of life skills.
Final Thoughts
Helping a person with a disability develop life skills is an ongoing process that requires patience, creativity, and support. By breaking tasks into simple steps, using visual aids, practicing through real-life scenarios, and fostering problem-solving abilities, you can empower individuals to become more independent and confident in their daily lives.
Remember, every individual is unique, and progress may look different for each person. Celebrate every step forward, no matter how small, and continue to provide the guidance and encouragement needed for their success.
With the right strategies and support, individuals with disabilities can thrive and develop the life skills they need to live more independently and confidently.